In the digital landscape, the rise of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has been nothing short of a rollercoaster journey. These digital assets, while basking in the limelight of popularity, have simultaneously weathered criticism from both the art community and the general public. As it is often the case with pioneering technologies, NFTs faced a skeptical reception initially, being branded as problematic, untested, and potentially detrimental to the world of art. However, the tides have since shifted, and the perception of NFTs now is more positive, or at least neutral. Intriguingly, this innovative technology has not only captivated digital enthusiasts and artists but also found a safe haven within the revered halls of prestigious museums and galleries. This prompts Digital Basel to state a pivotal question: Where does the truth lie amidst this unfolding narrative?
Let’s embark on a journey through history to uncover the reasons behind the initial controversy surrounding NFTs. Moreover, it will be a good opportunity to explore the actual benefits they offer to users and shed light on the role of companies like Digital Basel in this cutting-edge industry.
Deciphering NFTs
Non-fungible tokens, abbreviated as NFTs, constitute digital assets that symbolize various physical items, ranging from paintings to photographs, within the digital realm. They harness the capabilities of blockchain technology and smart contracts to furnish their holders with certificates of ownership, a traceable provenance, and automated trading mechanisms.
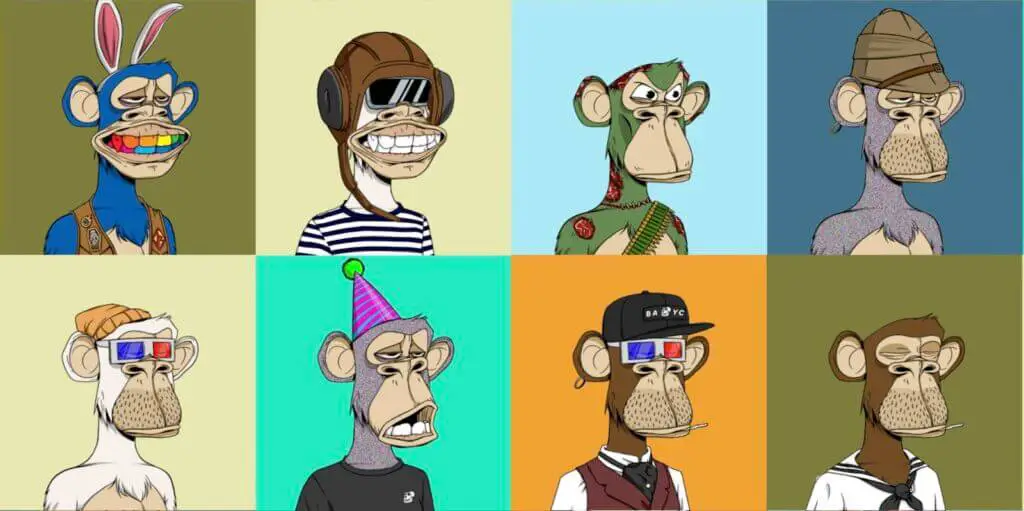

The collection has become very popular, and Bored Ape NFTs have been sold for millions of dollars.
While NFTs may initially come across as nothing more than digital images with inflated price tags, they offer a far-reaching spectrum of functionality. When an artist or art institution makes the decision to tokenize their creation, they essentially engrave a digital copy onto a blockchain. In this intricate process, they are tasked with specifying the token’s particulars, including its initial valuation, terms of use, description, and other pertinent details. Once this record is established, an event referred to as “minting” an NFT, the issuer can then upload and trade their token on a digital marketplace like OpenSea, Rarible, or, more art-oriented, DigitalBasel. Although these tokens may seem intricate for the sake of complexity, they fulfill a vital function by allowing both issuers and collectors to trace their origins, safeguard intellectual property, and confirm the authenticity of their acquisitions.
Digital Basel wants to remind that it is imperative to understand that while NFTs represent physical assets and can be procured online, they typically do not bestow ownership of the physical objects themselves. This unique feature empowers artists and art institutions to monetize their masterpieces without losing the originals.
Navigating the NFT Controversy
The world of NFTs assumed center stage when Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days” fetched $69 million. This moment propelled NFTs into the mainstream, fueled by media hype, an expanding digital audience, and blockchain enthusiasts. While some, including our team at Digital Basel, celebrated this novel digital format, others greeted NFTs with skepticism and apprehension, pinpointing four major concerns that revolve around:
Environment: At that juncture, numerous blockchains relied on energy-intensive proof-of-work mechanisms, giving rise to concerns about the environmental sustainability of NFT creation and trading.
Hype: The NFT market witnessed tokens, including those of questionable artistic merit, being traded for exorbitant sums, raising concerns of speculative bubbles.
Intellectual Property: In the early days, there was no platform like DigitalBasel. That’s why artists often discovered their digital works tokenized as NFTs without their consent, underscoring challenges in verifying the authenticity of NFTs.
Regulations: The relatively unregulated NFT marketplace paved the way for scams and fraudulent schemes, leaving investors and collectors vulnerable.
However, it would be a mistake to dismiss NFTs as a technology that poses universal threats, solely fosters speculation, and harms the environment. The reality is more nuanced. Like any innovation, NFTs require time and effort to evolve beyond the realms of novelty and fleeting trends. However, with the assistance of intermediaries like Digital Basel, this shift will become apparent in the near future.
Unveiling the Truth
Amidst the initial fervor, backlash, and market saturation, NFTs have firmly entrenched themselves in the market, owing to their diverse utility. When artists or art institutions tokenize their creations, they unlock various advantages:
- Separation of Digital and Physical: NFTs enable the sale of digital replicas independently of the physical originals.
- Provenance Verification: They offer a transparent ledger, ensuring the authenticity of the tokens.
- Automated Trading: NFTs streamline sales on digital marketplaces.
- Global Accessibility: The digital nature of NFTs makes them borderless assets, accessible and tradable worldwide. For example, art assets minted with the help of Digital Basel can be accessed from any point in the world where one can find an internet waypoint.
Furthermore, these digital assets find applications in virtual reality, augmented reality, and metaverse spaces, providing owners with unique experiences. This innovative revenue stream benefits all participants in the art market, especially as the digital user base continues to expand with the help of organizations such as Digital Basel.
While concerns such as environmental impact and speculation once loomed large, the NFT landscape has evolved. Some blockchains have shifted to more eco-friendly proof-of-stake mechanisms, and platforms similar to DigitalBasel have adopted more rigorous curation practices and collaboration with verified artists, mitigating intellectual property concerns.
Why Consider NFTs
Art institutions should consider embracing NFTs for several reasons:
Inclusivity: NFTs democratize art collecting by enabling a broader range of individuals to participate in the market, expanding outreach, and engaging a diverse community. Meantime, many intermediaries like Arcual or Digital Basel can amplify this outreach even further.
Transparent Provenance: NFTs provide a transparent and immutable ledger, assuring both issuers and collectors of artwork authenticity.
New Revenue Streams: NFTs offer a diversification of income sources, allowing art institutions to monetize art through direct sales and receive royalties on resales.
Global Reach: These borderless assets can be bought and sold worldwide, regardless of whether the initial platform was Digital Basel or any other marketplace.
Community Engagement: NFTs facilitate direct engagement with art enthusiasts, fostering online communities and enabling ecosystems in VR, AR, or metaverse spaces.
Contemporary Art Appreciation: NFTs tap into the interest of digital collectors in art’s capital appreciation and low loss rates, making valuable art assets more accessible.
Art institutions, however, should tread carefully, considering potential issues like environmental impact and speculation while formulating a strategy. Alternatively, they can seek the support of specialized organizations like Digital Basel or Arcual.
The Role of Specialized Organizations
In the realm of digital art, specialized organizations like Arcual and Digital Basel play essential roles. Arcual focuses on creating added value for existing artworks by supplying digital art dossiers to buyers. Digital Basel acts as a facilitator, assisting art institutions in finding their audience by offering a platform and marketing services, conducting due diligence, and ensuring a satisfactory experience for all parties involved.

With more than 200 galleries already benefiting from Digital Basel’s services, adopting NFTs becomes a smoother and more secure process. These organizations help mitigate industry challenges while expanding outreach.
In conclusion, NFTs are not the problematic technology that some critics paint them to be. While issues persist, the substantial benefits they offer, along with the contributions of associated organizations like Digital Basel, to art institutions are significant. Embracing NFTs requires a thoughtful and ethical approach, weighing potential concerns against the advantages they bring. The NFT art industry beckons, offering unique opportunities worth exploring.